NUTRIENT PRESENTATION
vitamin B6
Contained in: lobster, crayfish, meat, yeast, legumes, whole grains, nuts.
Form: Pyridoxal – 5 – phosphate
Origin: synthetic
Classification: Pharmacopoeia quality USP
Place of manufacture: China
Function: Co-enzyme for >100 enzymatic reactions
Risk groups: alcohol abuse, liver disease, use of oral contraceptives and medications for epilepsy or asthma [3].
ADVANTAGES
Vitamin B6 Facts & Knowledge
Supply in Germany according to the National Consumption Study II: 12% of men and 13% of women do not reach the recommended daily intake of vitamin B6 [9].
VITAMIN B6 AND ITS FUNCTIONS [7]
- Vitamin B6 is sensitive to light and heat. Up to 40% can be lost during cooking.
- The metabolically active forms of vitamin B6, pyridoxal-5′-phosphate (PLP) and pyridoxamine-5′-phosphate (PMP), act as cofactors of enzymes involved in the following processes:
VITAMIN B6 DURING PREGNANCY
- Due to the increasing protein requirement during pregnancy, the need for B6 also increases by 58% from the 4th month of pregnancy
- The additional requirement is intended to compensate for losses through breast milk and to replenish the mother's B6 reserves.
- Recommended intake increased by 58% from the 4th month onwards [7].
- According to the American Society of Neurologists, treatment with B6 is possible for nausea and vomiting [5].
- Studies have reported that PLP concentrations in pregnant women decrease by up to 65-75% in the third trimester. This is thought to be due to an accumulation of PLP on the fetal side [7, 8, 10].
- Studies on pyridoxine supplementation during pregnancy have shown that it can reduce the risk of preterm birth, nausea and vomiting in the mother, and the risk of orofacial clefts (cleft lip and palate) and cardiac malformations in the newborn. Better Apgar scores in the first minute and higher weight were also observed in the newborns [1, 2].
PLANT-BASED DIET
The need for vitamin B6 depends on the protein turnover in the body, as vitamin B6 is crucial for the breakdown and conversion of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins.
ACCEPTED HEALTH CLAIMS
- Vitamin B6 contributes to
normal cysteine synthesis
at - Vitamin B6 contributes to a
normal energy metabolism in - Vitamin B6 contributes to
normal functioning of the nervous system in - Vitamin B6 contributes to a
normal homocysteine metabolism in - Vitamin B6 contributes to a
normal protein and glycogen metabolism in - Vitamin B6 contributes to normal psychological function
- Vitamin B6 contributes to the normal formation of red blood cells
- Vitamin B6 contributes to
normal function of the immune system in - Vitamin B6 helps reduce fatigue and
fatigue in - Vitamin B6 contributes to the regulation of hormone activity
at
biomarkers
Note: Even mean values below 30 nmol/L are associated with a wide range of metabolic effects, including disturbances in plasma amino acid, lipid and organic acid profiles. Plasma concentrations of PLP decrease with age, during pregnancy (compared to non-pregnant women) and during inflammation [7].
< 20 nmol/l
20-30 nmol/l
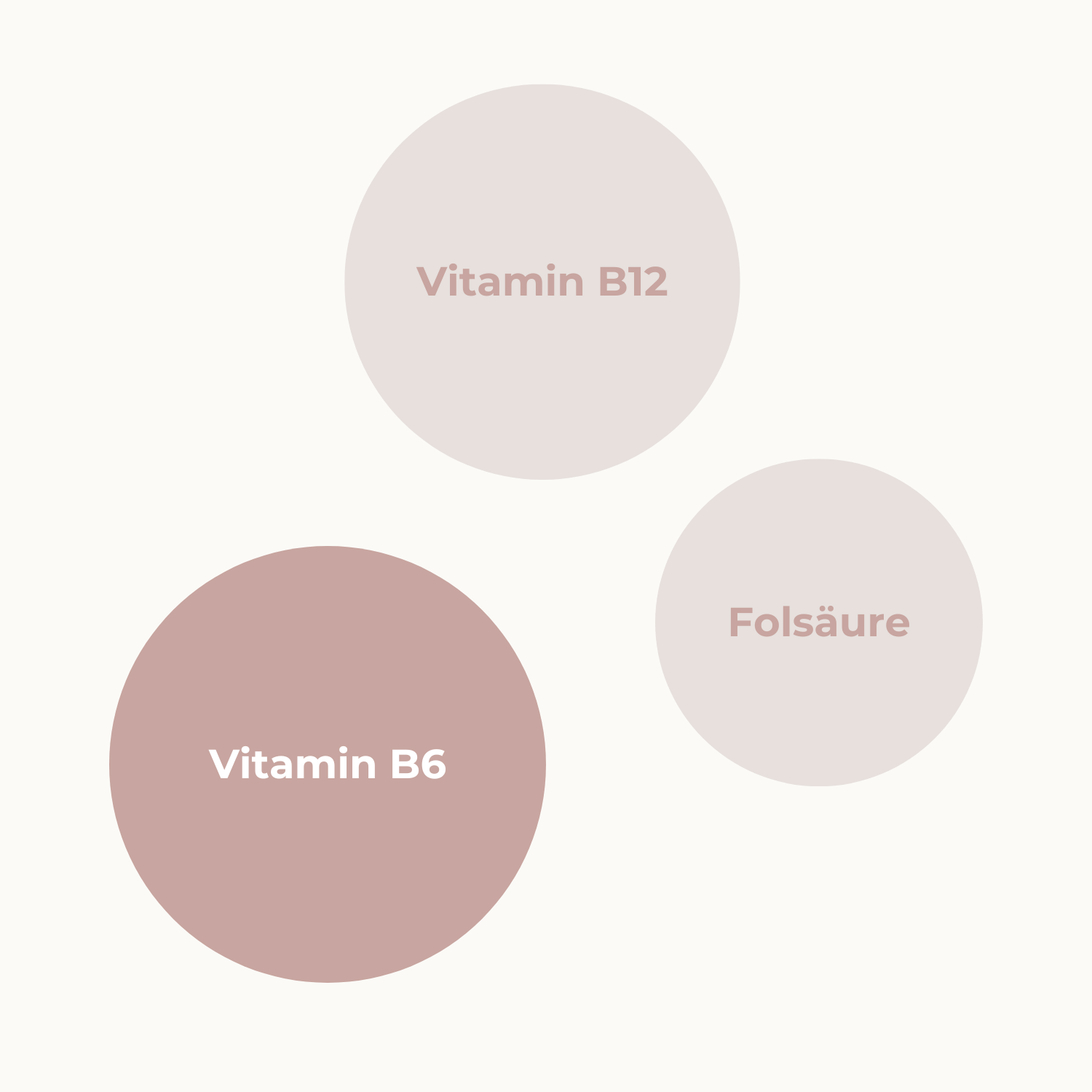
COLLEAGUES
Who does Vitamin B6 work with?
Folic acid, vitamin B12 and vitamin B6 are necessary for the detoxification of the vascular and neurotoxic amino acid homocysteine and for the formation of red blood cells.
FOR FURTHER READING
Evidence-based formulations
We use nutrients that are backed by a comprehensive body of research that is growing daily.