NUTRIENT PRESENTATION
Vitamin B3 / Niacin
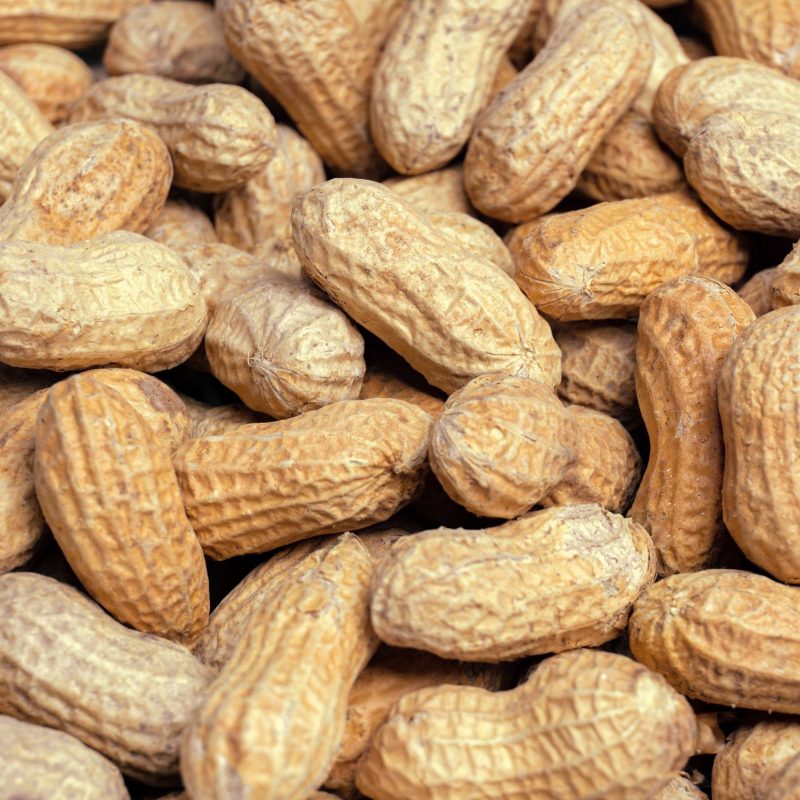
Contained in: meat, liver, fish, mushrooms, whole grain products
Form: Niacin / Nicotinamide
Classification: Pharmacopoeia quality Ph.Eur./USP
Origin: synthetic
Place of manufacture: China
Function: Building block of the coenzymes NAD and NADH
Risk groups: pregnant women, chronic alcohol consumption, anorexia, chronic diarrhea or liver cirrhosis [5].
ADVANTAGES
Vitamin B3 Facts & Knowledge
Supply in Germany according to the National Consumption Study II: 1% of men and 2% of women do not reach the recommended daily intake of niacin [7].
VITAMIN B3 AND ITS FUNCTIONS [6]
- Energy production during the breakdown of major nutrients.
- Niacin can be synthesized in the human body from the essential amino acid tryptophan.
- Approximately 60 mg of tryptophan yields 1 mg of niacin, defined as 1 mg of niacin equivalent (NE).
- Long-term insufficient intake of tryptophan and niacin can lead to the development of pellagra.
- Niacin is the precursor of the nicotinamide nucleotide coenzymes NAD and NADP.
- NAD and NADP act as coenzymes to catalyze redox reactions in the oxidative metabolic pathways, particularly in glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and the mitochondrial respiratory chain.
- NADP-bound enzymes are also found in fatty acid and steroid synthesis.
- NAD is also involved in calcium mobilization, cell signaling and DNA repair.
- NAD is essential for energy-producing reactions and NADP is essential for anabolic reactions.
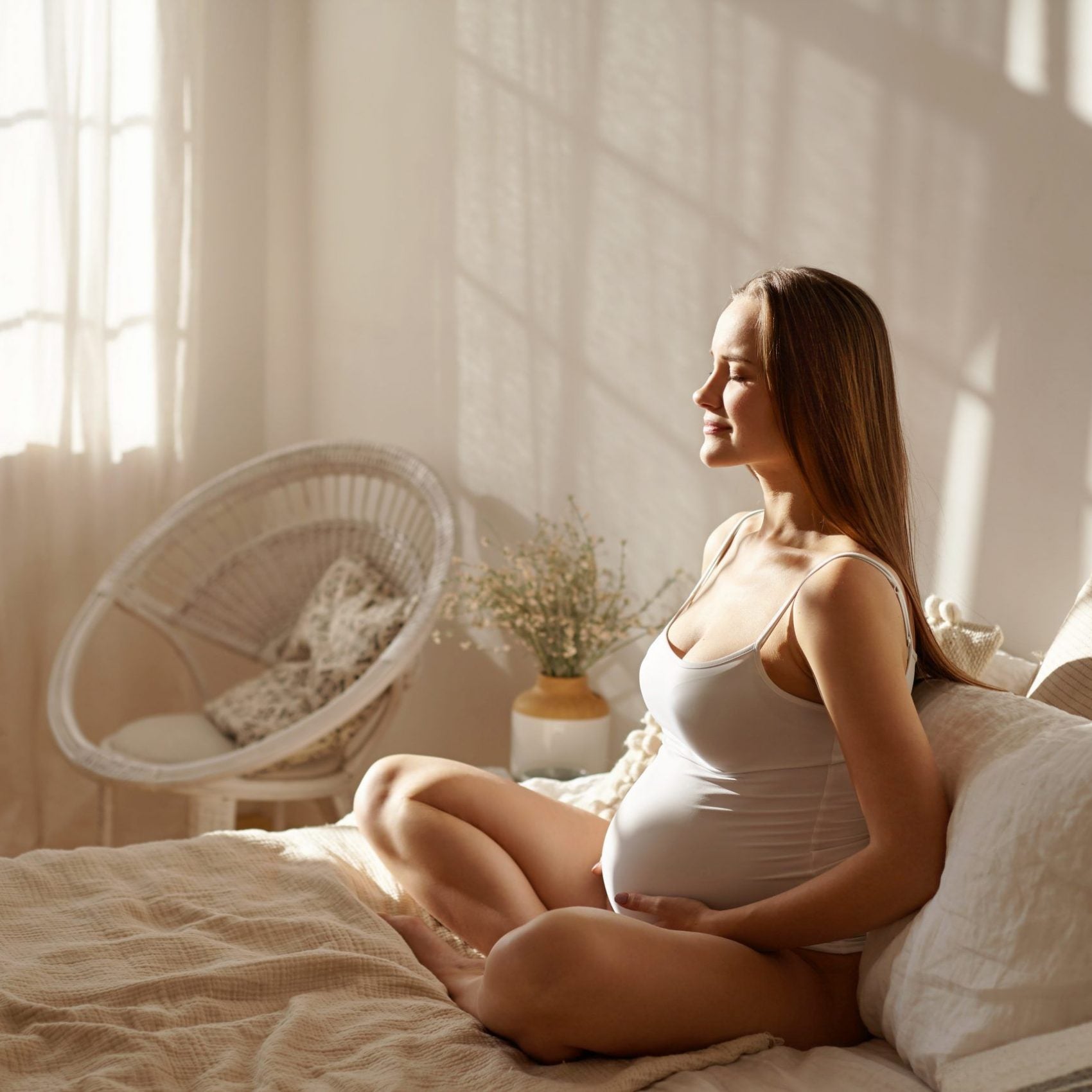
VITAMIN B3 DURING PREGNANCY
- The need for niacin is increased during pregnancy [5].
- Adequate intake of niacin reduces the risk of birth defects [2].
ACCEPTED HEALTH CLAIMS
- Niacin contributes to normal energy metabolism
at - Niacin contributes to the normal functioning of the nervous system
- Niacin contributes to normal psychological function
- Niacin contributes to the maintenance
normal mucous membranes in - Niacin contributes to the maintenance
normal skin - Niacin helps reduce tiredness and fatigue
PLANT-BASED DIET
- Niacin levels are sometimes lower in vegetarians than in omnivores [4].
- The body cannot absorb niacin as well from plant foods, such as grains, as it can from animal foods [5].
biomarkers
Based on available data, the European Food Safety Authority suspects that NAD concentration in erythrocytes may be a biomarker for niacin depletion caused by “low” NE intake (≤ 10.1 mg NE/day).
Note: However, based on the limited data available, no conclusion can be drawn regarding the relationship between erythrocyte NAD concentration and niacin requirement [6].
≤ 10.1 mg niacin equivalent/day is considered deficient
COLLEAGUES
Who does Vitamin B3 work with?
Like B1 and B2, niacin contributes to energy metabolism and the nervous system.
FOR FURTHER READING
Evidence-based formulations
We use nutrients that are backed by a comprehensive body of research that is growing daily.