NUTRIENT PRESENTATION
Vitamin B1 / Thiamine
Found in: whole grains, meat, fish, legumes (especially) soybeans.
Form: Thiamine mononitrate
Origin: synthetic
Classification: Pharmacopoeia quality Ph.Eur./USP
Place of manufacture: China
Function: involved in the formation of acetylcholine; coenzyme in carbohydrate and protein metabolism
Risk groups: chronic alcohol consumption, diabetics, seniors, morning sickness (hyperemesis gravidarum), gastrointestinal and liver diseases [7].
ADVANTAGES
Vitamin B1 Facts & Knowledge
Supply in Germany according to the National Consumption Study II: 21% of men and 32% of women do not reach the recommended daily intake of vitamin B1 [9].
VITAMIN B1 AND ITS FUNCTIONS [6]
- Note: Vitamin B1 is sensitive to heat: When heated, the thiamine content of foods drops by up to 70%
- B1 is important for the brain and nervous system because it is involved in the formation of neurotransmitters acetylcholine and gamma-aminobutyric acid acetylcholine.
- Coenzyme for enzymes involved in carbohydrate and branched-chain amino acid metabolism as well as in energy-producing reactions.
VITAMIN B1 DURING PREGNANCY
- Vitamins B1 and B2 are essential for fetal growth [1, 3, 4].
- Prolonged vomiting (hyperemesis) poses a risk for B1 deficiency [5, 7].
- The recommended intake for vitamin B1 increases by 20% in the first and second trimesters and by 30% by the third trimester and during breastfeeding [7].
ACCEPTED HEALTH CLAIMS
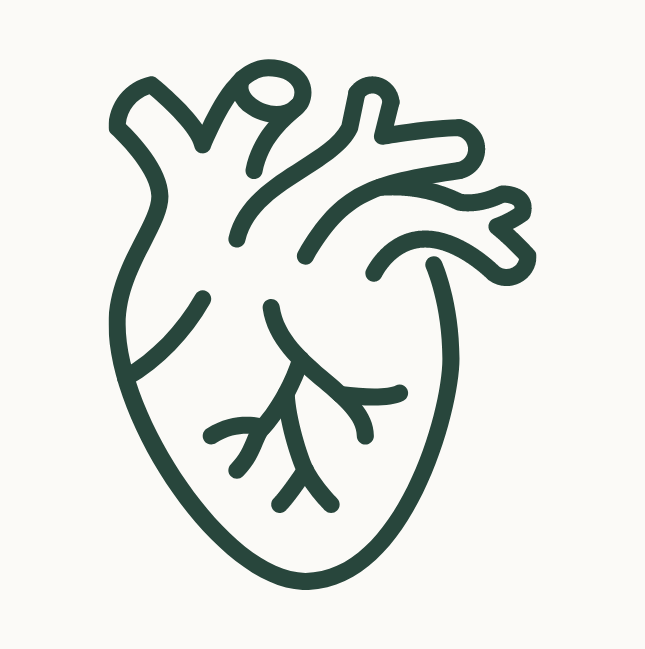
- Thiamine contributes to normal heart function
- Thiamine contributes to normal
psychological function in - Thiamine contributes to the normal functioning of the nervous system
- Thiamine contributes to normal energy metabolism
biomarkers
Note: Vitamin B1 acts as a cofactor for erythrocyte transketolase. Reduced activity of these enzymes in red blood cells indicates a vitamin B1 deficiency. The increase in transketolase activity in erythrocytes after addition of thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP effect) is considered a reliable indicator of vitamin B1 deficiency. An increase of more than 15% probably indicates a deficiency [6].
1.00-1.15
1.20-1.25
>1.25
COLLEAGUES
Who does Vitamin B1 work with?
Vitamin B1, together with the other B vitamins, contributes to normal energy metabolism and normal functioning of the nervous system.
FOR FURTHER READING
Evidence-based formulations
We use nutrients that are backed by a comprehensive body of research that is growing daily.